Adsorption behavior and mechanism of heavy metal ions by chicken feather protein-based semi-interpenetrating polymer networks super absorbent resin†
Abstract
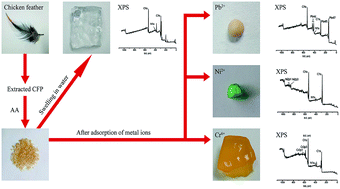
A novel chicken feather protein-g-poly(potassium acrylate)/polyvinyl alcohol (CFP-g-PKA/PVA) semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) super absorbent resin (SAR) was synthesized by graft copolymerization for the uptake of metal ions from aqueous solution. The influences of adsorption parameters, including pH, contact time, temperature, and initial concentrations, were investigated. The adsorption isotherms were described by Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption models. The adsorption kinetics were analyzed using pseudo-first- and second-order kinetic models and an intra-particle diffusion model. The results showed that the adsorption process was better represented by the Freundlich model, and the data obeyed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The maximum adsorption capacity was 170.3, 78.55, and 143.2 mg g−1 for Ni2+, Cr6+, and Pb2+, respectively. Calculation of the thermodynamic parameters indicated that the adsorption process was spontaneously endothermic. The laden metal ions on the surface of the super absorbent resin were validated by FTIR and XPS. FTIR and XPS analysis also explained the adsorption mechanisms, including chelation bonding, electrostatic interaction, and ion-exchange, with the action of functional groups, such as –COOH and –NH2. Adsorption–desorption experiments showed that at least 60% of the adsorption capacities of the SARs were retained after the fifth cycle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...