Direct hydroxylation of benzene to phenol using H2O2 as an oxidant over vanadium-containing nitrogen doped mesoporous carbon catalysts†
Abstract
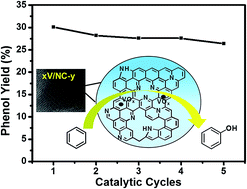
Highly ordered nitrogen doped mesoporous carbon (NC) was synthesized via a hard template method using hexamethylenetetramine as the precursor and KIT-6 as the template. The NC materials calcined at different temperatures were used as supports to prepare a series of vanadium containing catalysts by the impregnation method. The integration of the highly ordered three-dimensional (3D) mesostructure, the hydrophobic surface with an open π-conjugated system, the abundant defects introduced by nitrogen related functionalities, and the highly dispersed vanadium species made the catalysts highly efficient in the benzene hydroxylation reaction using H2O2 as an oxidant. By optimizing the preparation and reaction conditions, a maximum benzene conversion of 31.0% and a phenol selectivity of 97.2% were obtained over a 4.2V/NC-600 catalyst, which was superior to the activity of the vanadium supported two-dimensional (2D) hexagonal mesoporous carbon with an amorphous framework.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...