Characterization of hydrogenated graphite powder by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry†
Abstract
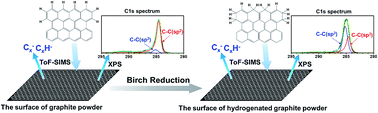
Hydrogenated graphite powder was obtained through Birch reduction of graphite powder and characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) at 500 °C. The sp3 carbons formed at the edges of the surface of the hydrogenated graphite powder exhibited an sp3 carbon peak in the XPS C1s spectrum. The sp3-to-sp2 carbon ratio calculated from the XPS spectra increased from 0.08 to 1.19 after hydrogenation. Two sets of peaks, the Cx− and CxH− ion series (where x = 1, 2, 3…), were identified in the ToF-SIMS spectra of both the graphite powder and hydrogenated graphite powder. The difference between these two spectra represented an increase in the normalized intensities of the H− and CxH− ions in the spectrum of the hydrogenated graphite powder, indicating the formation of more sp3 carbons on the surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...