Ammonia and iron cointercalated iron sulfide (NH3)Fe0.25Fe2S2: hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure, weak ferromagnetism and crossover from a negative to positive magnetoresistance†
Abstract
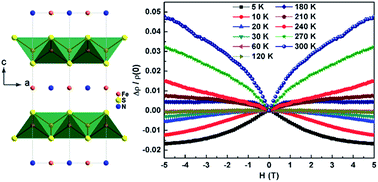
The discovery of superconductivity in anti-PbO-type FeS has aroused a renewed interest in the intercalation compounds of FeS. Here we report a novel intercalation compound of FeS with the chemical composition of (NH3)Fe0.25Fe2S2, which is synthesized via a new hydrothermal reaction. This material crystallizes in the tetragonal space group I4/mmm, preserving the FeS tetrahedral layers with ammonia and excess iron forming planes in between. The microstructure and thermal stability of the sample were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and thermogravimetric analyses (TGA). These results suggest that (NH3)Fe0.25Fe2S2 is not sensitive to electron beam irradiation and is more thermally stable than the other ammonia intercalated iron selenide superconductors. Physical property measurements show that it is a ferromagnetic semiconductor. By using first-principles calculations we assess that the low-temperature ferromagnetism originates from the interlayer rather than the intralayer iron. The transport properties at low temperatures are dominated by electron-like carriers and the sign reversal and strong temperature dependence of the Hall coefficient may be caused by a multi-band effect. Most importantly, an unusual crossover from negative to positive magnetoresistance with increasing temperature was identified, which reveals relatively strong coupling between carriers and magnetic moments as well as disorder.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...