Low-temperature synthesis of mesoporous ZnTiO3–graphene composite for the removal of norfloxacin in aqueous solution
Abstract
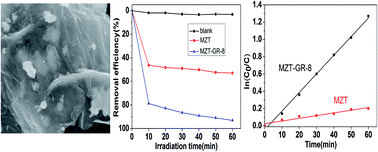
A novel mesoporous perovskite-type ZnTiO3–graphene (MZT–GR) material was successfully fabricated via a two-step process in this paper. Initially, mesoporous ZnTiO3 (MZT) was prepared by an evaporation-induced self-assembly method using a polycarboxylate superplasticizer as a template at 500 °C, which was subsequently decorated on graphene using a hydrothermal method. The obtained products were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis (TG), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-visible DRS), and Raman spectroscopy. A series of photocatalysis experiments demonstrated that MZT–GR exhibited excellent photocatalytic performance. The degradation efficiency of norfloxacin reached 93% over MZT–GR composites under visible light irradiation for 60 min as compared with pure MZT (53%), which was attributed to MZT–GR's great adsorptivity of contaminants, enhanced light absorption and efficient charge separation properties collectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...