Amplified sensitization of Er3+ luminescence in silica by AuN quantum clusters upon annealing in a reducing atmosphere
Abstract
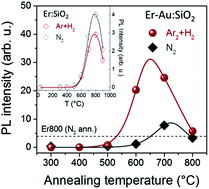
Finding effective strategies for improving the luminescence emission performance of Er3+ ions in silica is of paramount importance for the realization of efficient Er-based nanophotonic devices. To this aim, in the present work the sensitization mechanism of room temperature Er3+ luminescence by AuN quantum clusters, upon annealing in a reducing atmosphere, was investigated by photoluminescence characterization of Er–Au co-implanted samples in which Au ions were implanted at a low fluence of 3.4 × 1014 Au+ per cm2. The role of the annealing atmosphere was unveiled by comparing the emission properties of samples thermally treated in reducing and inert atmospheres. A significant amplification of the Er3+ sensitization efficiency (up to a 6× enhancement of the photoluminescent intensity) was revealed upon annealing in a reducing atmosphere and the possibility to get efficient room temperature Er3+ luminescence from Er–Au co-implanted samples with only a limited amount of sensitizing agents was demonstrated and discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...