Synthesis of carbon nanoparticle embedded graphene for sensitive and selective determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid in biological fluids†
Abstract
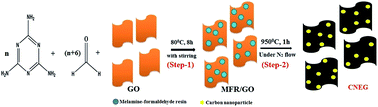
We have prepared carbon nanoparticle embedded graphene (CNEG) by carbonizing a ternary composite of GO/melamine-formaldehyde resin/Zn(OAc)2. CNEG is characterized by TEM, FESEM, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy and BET. The CNEG showed narrow distributed pores with diameters from 1.55 to 7.40 nm and has a high surface area (241 m2 g−1). The CNEG is introduced as a substitute for graphite paste (GP) electrode with better performance. A CNEG modified GP (CNEG/GP) electrode shows better electrocatalytic oxidation towards ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA) than both a bare GP electrode and a thermally reduced graphene oxide modified graphite paste (TRG/GP) electrode. Two well-separated voltammetry peaks are obtained using the CNEG/GP electrode in differential pulse voltammetry measurements and the corresponding peak separation between AA and DA is 192 mV facilitating simultaneous determination of these two biomolecules. Under optimized experimental condition, the linear ranges of determinations of DA and AA are found to be 0.07–200 μM and 25–2700 μM respectively. The lower detection limits for DA and AA are 50 nM and 520 nM respectively. Furthermore, the CNEG/GP electrode shows good reproducibility and chemical stability. It is also tested for the analysis of urine, serum and pharmaceutical products with better sensitivities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...