Sustainable production of activated carbon spheres from ethyl cellulose†
Abstract
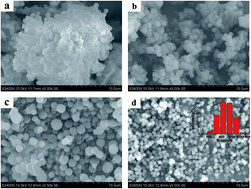
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is an effective and sustainable way to covert biomass into functional carbonaceous materials. Effects of condition parameters on the morphology and particle size distributions were evaluated. However, the absence of porosity of HTC materials limits their wide applications. Activation of HTC materials could solve this problem. Traditional activation methods, which use strong base or acid as activating agent, could lead to pollutions. Here, we prepared microporous activated carbon spheres from ethyl cellulose under static air atmosphere. The resultant activated carbon spheres were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), FT-IR spectrometer, X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and nitrogen adsorption. Results reveal that the obtained carbon spheres show smooth surface, good dispersion and abundant surface functional groups. In addition, the spherical carbon exhibits high adsorption abilities for different kinds of dyes, which is important for environment protection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...