Detergent-free decellularization of bovine costal cartilage for chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose mesenchymal stem cells in vitro†
Abstract
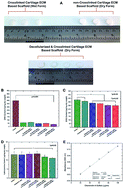
In this study, we report a novel, detergent-free decellularization protocol for the preparation of intact cartilage ECM-based scaffolds (CEbS) during an effective decalcification process. On treatment with 10 mM Na2EDTA, the amount of calcium lost was around 55% ± 5% (percent ± S.D.%) (n = 3) and nearly 84% of the nuclear material was removed; however, the most effective removal was observed on treatment with 10 mM Na2EDTA combined with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 48 hours. Notably, our proposed method decreased the GAG content by only 5% compared to untreated CEbS (380.37 ± 16.02 μg mg−1 dry weight). There was no significant difference in hydroxyproline content between the untreated (13.04 ± 1.51 μg mg−1 dry weight) sample and our proposed method (12.95 ± 1.55 μg mg−1 dry weight). The scaffold morphology and cell attachment were evaluated using SEM micrographs, and the cells that were inoculated with detergent-free decellularized CEbS for 14, 21 and 28 days covered the scaffold area, including the porous cavities. Microscopic observations showed that the cell density increased day by day and there was no cytotoxic evidence for the scaffolds, which is a desirable environment for cells. The histochemical and immunohistochemical assessments are supported by glycosaminoglycan and hydroxyproline assays. The proposed detergent-free decellularization technique could be a promising method for cartilage tissue regeneration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...