Unusual surface and solution behaviour of keratin polypeptides†
Abstract
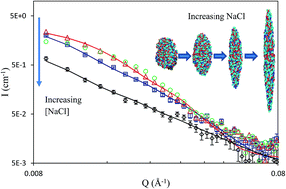
Keratins are filament proteins, but we report in this work that water-soluble keratin polypeptides hydrolyzed from wool could readily adsorb onto the surface of water and could thus be used as surface active biomaterials. Neutron reflection measurements with the help of deuterium labelling were used to determine the adsorbed amount and distribution of the polypeptide layers formed. It was found that the interfacial layers were comprised of two main regions, a dense top layer of 18–25 Å and a loose bottom layer of 25–30 Å. Half of the top dense layer was exposed to air with the remainder of the top layer and the diffuse bottom layer immersed in the aqueous solution. Both the volume fraction and the layer thickness increased with keratin solution concentration as did the adsorbed amount which was seen to plateau just above 2 mg m−2 at approximately 0.1 g dm−3 (2.1 μM). Increase in [NaCl] led to reduced surface adsorption, accompanied with the thinning of the top layer. Cryo-TEM imaging revealed that the keratin aggregates had an ellipsoidal structure with radii ranging from 60 Å to 220 Å. The ellipsoidal shape was well supported by SANS, with the major radius of 140 Å and the minor radius of 60 Å. With increasing [NaCl], the ellipsoids became thinner but longer, a feature consistent with the observed trend from surface adsorbed layer. This unusual behaviour could be explained by the electrostatic screening effect. As the salt concentration increased, the polypeptide chains became stiffer and more readily aligned, resulting in thinner layers and longer aggregates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...