Highly sensitive and selective optical detection of lead(ii) using a label-free fluorescent aptasensor
Abstract
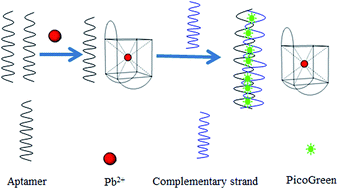
Lead (Pb) is a heavy metal that does great harm to human bodies through its accumulation in the food chain. It remains a challenge to use environment-friendly and biocompatible materials to sensitively detect lead in organisms and aquatic ecosystems. To achieve highly sensitive and selective Pb2+ detection, a sensor based on ultra-sensitive double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) specific dye PicoGreen and label-free oligonucleotides was reported. The principle of this method is that the Pb2+ induced a structural change of G-rich thrombin aptamer from random coil to G-quadruplex, which prevented its binding to its complementary sequences to form dsDNA and caused a fluorescence intensity decrease with PicoGreen. The results showed that this method satisfied the requirement of the maximum residue limit (MRL) of Pb2+ and could detect Pb2+ at a lowest concentration of 1 ng mL−1 within a dynamic range of six orders of magnitude. Since the aptamer was highly specific, this method showed high Pb2+ selectivity against eight other metals. Finally, the proposed assay was successfully validated by determining Pb2+ in water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...