Nanocrystalline MnO2 on an activated carbon fiber for catalytic formaldehyde removal†
Abstract
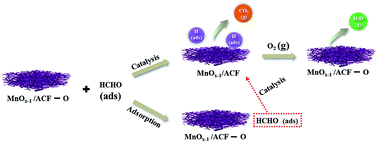
Three different types of nanocrystalline MnO2, namely, α-MnO2, γ-MnO2 and δ-MnO2, were successfully synthesized via a co-precipitation method, which has the advantages of easy preparation, low cost, size uniformity and excellent crystallinity. It also avoids operating at high temperatures and pressures. The nanocrystalline MnO2 were then tested for formaldehyde catalytic oxidation at 25 °C. The results suggested that δ-MnO2 had the highest catalytic activity. Hence, δ-MnO2 was synthesized using the same method to modify an activated carbon fiber (ACF) substrate. Further tests showed that the as-prepared MnO2/ACF samples can significantly improve the removal of formaldehyde at room temperature. The MnO2 content in MnO2/ACF had great influence on the breakthrough time and we found that the MnO2 content did not best perform at greater magnitudes but were optimal at 16.12 wt%. The formation method developed in this study may become a promising technique to improve the catalytic activity in formaldehyde removal.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...