Organic–inorganic hybrid polyoxometalate and its graphene oxide–Fe3O4 nanocomposite, synthesis, characterization and their applications as nanocatalysts for the Knoevenagel condensation and the synthesis of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones†
Abstract
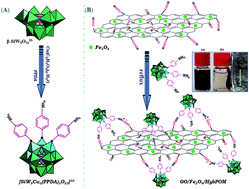
The simple and high yield synthesis of H6Cu2[PPD]6[SiW9Cu3O37]·12H2O (PPD = p-phenylenediamine) as a new organic–inorganic hybrid polyoxometalate is reported. The new compound consists of trimetal-substitution polyoxometalate of A-β-SiW9Cu3O3710−, water molecules and coordinated and noncoordinated PPD molecules. H6Cu2[PPD]6[SiW9Cu3O37]·12H2O was firmly grafted on graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. These nanocomposites were characterized by elemental analyses, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectrum (XPS), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), and alternating gradient force magnetometer (AGFM). The results indicate that the size range of the nanoparticles are between 20 and 60 nm. The catalytic activity of H6Cu2[PPD]6[SiW9Cu3O37]·12H2O and the magnetically reusable nanocomposite of GO@Fe3O4@H6Cu2[PPD]6[SiW9Cu3O37]·12H2O were investigated in the Knoevenagel condensation and synthesis of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...