One-step electrochemical fabrication of a nickel oxide nanoparticle/polyaniline nanowire/graphene oxide hybrid on a glassy carbon electrode for use as a non-enzymatic glucose biosensor†
Abstract
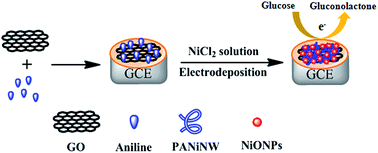
We propose here a novel non-enzymatic glucose biosensor composed of a nickel oxide nanoparticle/polyaniline nanowire/graphene oxide hybrid composite on a glassy carbon electrode (NiONP/PANiNW/GO/GCE). The composite, prepared by mixing aniline with graphene oxide (GO) together, was transferred onto the surface of a bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE). This was then immersed in deoxygenated 50 mM NiCl2 solution and electrodeposited at −0.8 V for 400 s to obtain the modified electrode, NiONP/PANiNW/GO/GCE. We characterized the morphology and electrochemical performance of the modified electrode using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and cyclic voltammetry (CV), respectively. We found that the NiONP/PANiNW/GO/GCE exhibits higher electrocatalytic activity for glucose oxidation than a nickel oxide nanosheet/graphene oxide modified glassy carbon electrode (NiONS/GO/GCE) in alkaline solution. The sensitivity of the sensor towards glucose oxidation is 376.22 μA mM−1 cm−2 with a linearity range of 2 μM to 5.560 mM and a detection limit of 0.5 μM (S/N = 3). The sensor selectively detects glucose in the presence of common interfering species such as ascorbic acid, uric acid and dopamine. Furthermore, we examined the applicability of this modified electrode as a sensing probe for the detection of glucose concentration in fetal bovine serum. We conclude that the highly selective and sensitive NiONP/PANiNW/GO/GCE based non-enzymatic glucose sensor has the potential to be applied to the accurate measurement of glucose levels for various practical purposes such as clinical diagnosis and food analysis, etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...