Efficient planar perovskite solar cells prepared via a low-pressure vapor-assisted solution process with fullerene/TiO2 as an electron collection bilayer†
Abstract
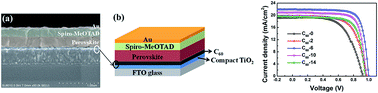
In perovskite solar cells (PSC), electron collection layers play a critical role in blocking holes and transporting electrons for high performances. In this study, a fullerene layer was introduced by a solution-process method between the TiO2 layer and CH3NH3PbI3 layer, which was synthesized via a low-pressure vapor assisted solution process. Both the fullerene and TiO2 layers acted as electron collection layers together. The results show that the electron collection bilayer dramatically enhances cell performance even with part of the fullerene dissolved in DMF solution. The optimized PSC can achieve a PCE of 16.58%, with a FF of 75.91% measured under reverse voltage scanning. For PSCs only using TiO2 as the collection layer, the average PCE and FF values are 10.2% and 58.6%, respectively. When fullerene was used as a single electron collection layer, the PCE is only 4.29%, because of the incomplete coverage of fullerene on the FTO substrate. Additionally, PSCs with fullerene interface layers showed far less hysteresis than reference cells without fullerene layers. Analysis of the equivalent circuit of devices and fluorescence lifetime measurements focusing on the CH3NH3PbI3 film with an electron extraction layer confirm that in our device configuration fullerene facilitates electron injection from CH3NH3PbI3 into the compact TiO2 layer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...