HfO2 nanodots incorporated in TiO2 and its hydrogenation for high performance dye sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
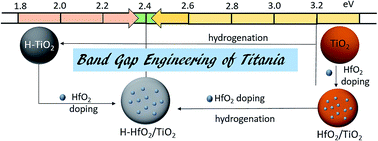
Black titania (H-TiO2) as a photoanode material has attracted huge attention due to its extremely high optical absorption in the visible region. Herein, black TiO2 doped with HfO2 shows ∼45.7% higher photo-conversion efficiency than H-TiO2 under identically similar conditions. The incorporation of HfO2 nanodots increased the optical scattering in H-TiO2 only when it underwent hydrogenation along with TiO2. Hafnia-doped TiO2 (HfO2/TiO2) is synthesized by a combination of simple sol–gel and hydrothermal method followed by thermal annealing under controlled hydrogen atmosphere. The hydrogenated H-(TiO2/HfO2) exhibited very high optical absorption but slightly lower than H-TiO2 due to light scattering by HfO2 nanodots. We observed a sharp decrease in optical band gap of TiO2/HfO2 from 3.2 to 2.4 eV up on hydrogen annealing, which is important in solar applications as demonstrated by the fabrication of high efficiency dye sensitized solar cells (DSSC).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...