High performance CO2 filtration and sequestration by using bromomethyl benzene linked microporous networks†
Abstract
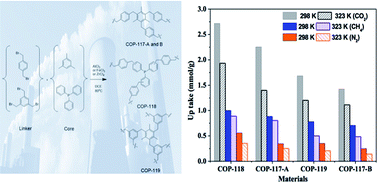
Porous solid sorbents have been investigated for the last few decades to replace the costly amine solution and explore the most efficient and economical material for CO2 capture and storage. Covalent organic polymers (COPs) have been recently introduced as promising materials to overcome several issues associated with the solid sorbents such as thermal stability and low gas capturing capacity. Herein we report the synthesis of four COPs and their CO2, N2 and CH4 uptakes. All the presented COP materials were characterized by using an elemental analysis method, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy techniques. The physical properties of the materials such as surface area, pore volume and pore size were determined by BET analysis at 77 K. All the materials were tested for CO2, CH4 and N2 adsorption through a volumetric method using magnetic sorption apparatus (MSA). Among the presented materials, COP-118 has the highest surface area of 473 m2 g−1 among the other four materials and has shown excellent performance by capturing 2.72 mmol g−1 of CO2, 1.002 mmol g−1 of CH4 and only 0.56 mmol g−1 of N2 at 298 K and 10 bars. However the selectivity of another material, COP-117-A, was better than that of COP-118. Nevertheless, the overall performance of the latter has indicated that this material can be considered for further exploration as an efficient and cheaply available solid sorbent compound for CO2 capture and separation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...