Quaternized N-chloramine coated magnetic nanoparticles: a trifecta of superior antibacterial activity, minimal residual toxicity and rapid site removal†
Abstract
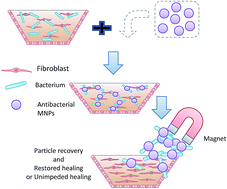
We propose a new and highly effective tool to add to the ever shrinking toolbox for combating infections caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria; N-chloramine and quaternized N-chloramine were coated onto iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles to generate antibacterial MNPs. Two differently-sized primary iron-oxide nanoparticles (3 nm and 10 nm) were synthesized and coated with silica and (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane, allowing subsequent introduction of N-chloramine precursors – dimethyl hydantoin (DMH) and quaternized dimethyl hydantoin (QDMH). The functionalized MNPs (MNP@DMH and MNP@QDMH) have a clear core–shell structure as evidenced by TEM images. Fe3O4 was identified (by combining X-ray diffraction with Mössbauer spectroscopy) to be the iron oxide in the 10 nm MNPs, while γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 were the 3 nm MNP's oxide phases. Both MNPs (3 nm and 10 nm) have good magnetic responses, with saturation magnetizations of 40 ± 4 emu g−1 and 65 ± 2 emu g−1, respectively. Chlorination activated the antibacterial function and yielded two antibacterial MNPs: MNP@DMCl and MNP@QASCl. At the equivalent [Cl+] of 50 ppm, both coatings demonstrated fast inactivation of the model bacteria methicilin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and multi-drug resistant (MDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa. For either size of primary MNPs, MNP@QDMCl is more effective than MNP@DMCl. A hand-held magnet could quickly remove >99% of the functionalized MNPs from a wound simulant within 2 minutes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...