Characterisation of composite films fabricated from collagen/chitosan and collagen/soy protein isolate for food packaging applications†
Abstract
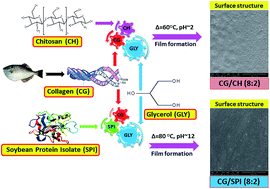
This study was undertaken to evaluate the potential of collagen/chitosan (CG/CH) and collagen/soy protein isolate (CG/SPI) composite films for food packaging applications. Two types of composite films at different blend ratios of CG/CH or CG/SPI (10 : 0, 8 : 2, 6 : 4, 5 : 5 and 0 : 10%, w/w) using 30% (w/w) glycerol as plasticiser were prepared and characterised. The results of mechanical tests of the CG/CH composite films displayed higher elongation at break point (EAB), but lower tensile strength (TS) and modulus of elasticity (E), compared to the CG film (P < 0.05). Conversely, the CG/SPI composite films exhibited lower EAB, but greater TS and E values (P < 0.05) compared to the CG film. Water vapour permeability (WVP) increased markedly in the CG/CH composite films; whilst it was found to decrease in CG/SPI composite films at the different blend ratios tested (P < 0.05). Transparency values and water solubility of CG/CH and CG/SPI composite films were decreased substantially, compared to the CG film (P < 0.05). Lower light transmission was observed in all composite films in ultraviolet (UV) and visible regions (200–800 nm), indicating improved UV blocking capacity. Intermolecular interactions through hydrogen bonding among polymeric components were dominant in the CG/SPI (8 : 2) composite film as elucidated by FTIR analysis. Thermo-gravimetric curves demonstrated that CG/CH (8 : 2) and CG/SPI (8 : 2) composite films exhibited lower heat susceptibility and weight loss (%), as compared to the CG film in the temperature range of 30–600 °C. DSC thermograms suggested that the compatible blend of CG/SPI (8 : 2) rendered a solid film matrix, which consisted of highly ordered and aggregated junction zones. SEM micrographs revealed that both CG/CH (8 : 2) and CG/SPI (8 : 2) composite films were slightly rougher than the CG film, but no apparent signs of cracking and layering phenomena were observed, thereby highlighting their potential use as biodegradable packaging materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...