Synthesis and effects of oxadiazole derivatives on tyrosinase activity and human SK-MEL-28 malignant melanoma cells†
Abstract
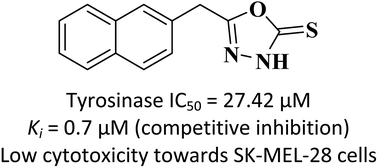
Melanin is a form of pigment that gives colour to human skin, hair and eyes. Whilst it protects against skin damage from the sun, accumulation of excessive amounts of epidermal melanin can lead to various dermatological disorders. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of three selected oxadiazoles on the o-diphenolase mushroom tyrosinase activity and their cytotoxic effects on SK-MEL-28 malignant melanoma cells. The results showed that compounds 1, 2 and 3 exhibited significant inhibition on the diphenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase with IC50 values of 40.46 μM, 27.42 μM and 32.51 μM, respectively. Further kinetic studies revealed that compounds 1 (Ki = 3.8 μM) and 3 (Ki = 3.9 μM) exhibited a mixed-type inhibition while compound 2 (Ki = 0.7 μM) displayed a competitive-type inhibition as suggested by the Lineweaver–Burk plots. Molecular docking and dynamics simulations were also performed to understand the binding behaviour of compound 2 in the active site of tyrosinase. Finally, all three compounds displayed relatively low cytotoxicity to SK-MEL-28 cells up to 100 μM treatment via MTT assay.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...