Computational study of the binding orientation and affinity of PPARγ agonists: inclusion of ligand-induced fit by cross-docking†
Abstract
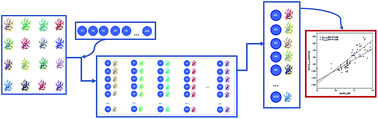
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) comprise a family of three nuclear receptor isoforms (γ, β/δ, α) which are key regulators of metabolism and inflammation. A series of potent PPARγ agonists with high chemical diversity and variable activities have been reported in recent years; however, few molecular atomistic studies have been carried out to describe the formation of the complexes. In this work, the docking of several potent agonists (organized into three sets) were performed inside the binding site of PPARγ and quantitative correlations between the obtained scoring energy functions and experimental biological activities were determined using the Glide and MM/GBSA methods. In silico experiments were achieved using a cross-docking protocol which includes sixteen PPARγ crystallographic structures. The studied ligands were positioned at the previously described binding pocket establishing interchangeable hydrogen bonds with key residues. Significant correlations (R2 > 0.6) were reported for the three studied sets using different methods. The use of several representative protein conformations for cross-docking, indicates that the induced-fit effects on the residues in the binding site have to be considered to plan docking experiments in PPARγ.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...