Photoelectrochemical properties of Ti-doped hematite nanosheet arrays decorated with CdS nanoparticles
Abstract
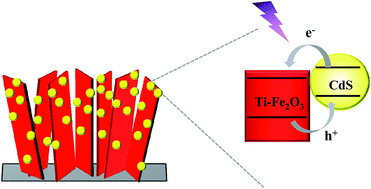
Hematite (α-Fe2O3), with a relatively narrow bandgap (2.0–2.2 eV), is well-suited for potential application as a photoanode in photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells. Unfortunately, it suffers from severe bulk carrier recombination and low conductivity. This study provides a way to overcome these shortages by constructing a novel electrode system comprised of vertically aligned Ti-doped hematite nanosheet arrays decorated with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles (Ti-Fe2O3/CdS). Ti doping improves the conductivity of hematite and simultaneously extends the spectral responsive range. The incorporation of CdS nanoparticles further facilitates the charge separation and transfer process. Subsequently, the fabricated Ti-Fe2O3/CdS electrode achieves 6-fold enhancement of photocurrent density with respect to pristine Fe2O3 and excellent operation stability. Meanwhile, an obvious negative shift of photocurrent onset potential by 500 mV is observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...