Effect of Ce doping into ZnO nanostructures to enhance the phenolic sensor performance
Abstract
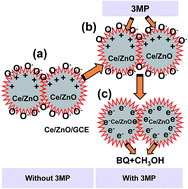
Various Ce-doped ZnO nanostructures (Ce/ZnO NSs) were prepared by a facile wet chemical method using reducing agents in alkaline medium. The Ce/ZnO NSs were characterized by UV/vis, FT-IR, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (XEDS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The Ce/ZnO NSs were deposited onto flat glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with conducting Nafion binders to produce a sensor that has a fast response towards selective 3-methoxyphenol (3MP). Characteristics including higher sensitivity, lower detection limit, better reliability, good reproducibility, ease of integration, long-term stability, high selectivity, and enhanced electrochemical performance were investigated in detail at room conditions. The calibration plot is linear (r2 = 0.9879) over a large concentration range (0.9 nM to 0.9 mM). The sensitivity and detection limit was calculated as ∼94.937 μA cm−2 μM−1 and 11.5 ± 0.2 pM (at a signal-to-noise-ratio [SNR] of 3), respectively. Finally, the efficiency of the proposed chemisensor can be applied and effectively utilized for the detection of various toxic chemical compounds in the environment with acceptable and reasonable results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...