Controlling the magnetic properties of polymer–iron oxide nanoparticle composite thin films via spatial particle orientation†
Abstract
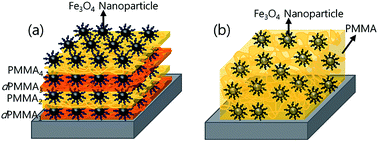
We investigated the effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticle orientation on the magnetic properties of hybrid polymer nanocomposite thin films. A multilayer thin film consisting of alternating layers of polymers and assembled iron oxide nanoparticles was prepared by spin coating and Langmuir–Blodgett techniques. Transmission electron microscopy and neutron reflectivity measurements were employed to determine structural information related to the lateral orientation of the Fe3O4 nanoparticle monolayer and the layered architecture along the depth of the multilayer, respectively. The magnetic properties of the hybrid multilayer were characterized by SQUID magnetometry and compared with the properties of a spin-coated polymer nanocomposite thin film containing homogenously dispersed Fe3O4 nanoparticles. We found that the closely-packed monolayer structure of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles changed the magnetic properties on account of the dipolar interactions between particles, whereas the homogeneously-dispersed nanoparticles embedded in the polymer matrix exhibited zero remanent magnetization and coercivity due to isolation of the nanoparticles and lack of dipolar interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...