Graphene quantum dots from fishbone carbon nanofibers†
Abstract
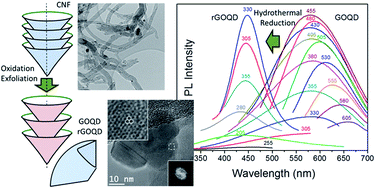
Graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQD) were obtained from fishbone carbon nanofibers (CNF) using a modified Hummers' method followed by ultrasound assisted exfoliation. Owing to its arrangement in accessible small sp2-carbon domains, CNF is a promising precursor for high yield GOQD obtention. The suspension was subjected to further separation by degressive differential centrifugation obtaining fractions of different sizes and oxidation states. The resulting graphene oxide-based products consisted of a mixture of expanded CNF, few-layer graphene oxide sheets and GOQD, the latter accounting for a yield of 42 wt% with respect to the initial CNF weight. The photoluminescence properties were dependent on the size and the oxidation state of each fractionated graphene oxide-based suspension. GOQD showed an excitation-dependent photoluminescent emission with a maximum at 578 nm (yellow) for an excitation of 455 nm. After hydrothermal reduction, reduced GOQD (rGOQD) exhibited bright violet photoluminescence at 448 nm for 330 nm of excitation due to the removal of hydroxyl and epoxide groups from basal planes of the graphene network. Furthermore, the quantum yield of GOQD and rGOQD were measured and reached values of 5.5 and 7%, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...