Investigation into the mechanism of polyoxotungstates-catalyzed cyclooctene epoxidation by ESI-MS†
Abstract
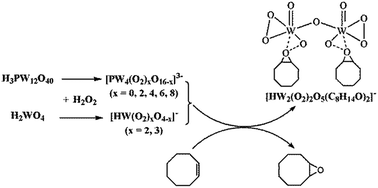
The reaction process of cyclooctene epoxidation was real-time monitored by ESI-MS using H3PW12O40 and H2WO4 as catalysts. By observing the species changes of the catalysts in the reaction solutions and the combination of catalysts with the substrate, a catalytic reaction mechanism of polyoxometalate clusters was proposed from the aspect of aggregation and dissociation. When H3PW12O40 was used as the catalyst, it was degraded into minor peroxo-species [PW4O16−x(O2)x]3− (x = 0, 2, 4, 6, 8) which performed as the active center of the epoxidation of cyclooctene. When H2WO4 was used as the catalyst, it reacted with H2O2 and generated mononuclear tungsten peroxo-species [HWO2(O2)2]− and [HWO2(O2)3]−. After the addition of cyclooctene, the peroxo-species catalyzed the epoxidation of cyclooctene, generating 1,2-epoxycyclooctane and combining with 1,2-epoxycyclooctane to form the intermediate [HW2(O2)2O5(C8H14O)2]−.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...