Carbon dots in ZnO macroporous films with controlled photoluminescence through defects engineering†
Abstract
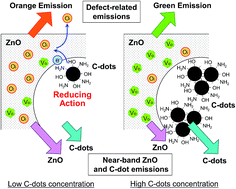
Carbon-dots (C-dots) nanocomposites represent a new frontier for highly efficient light-emitting materials with tunable colors in a wide range of the visible spectral region. We have developed a C-dots–ZnO system and the emission is finely controlled through material processing. The C-dots, besides being fluorophores, become a tool for modulating the defects in a ZnO matrix through chemical interactions. Macroporous ZnO films have been prepared via a hard templating route using mesoporous silica spheres which allows full crystallization of the ZnO framework and post-impregnation of large amounts of C-dots within the porous matrix. The photoluminescence spectra are given by a combination of different contributions: C-dots, UV near-band and defect-related ZnO emissions. The reducing action of the C-dots in the ZnO porous matrix allows engineering of the defect-related ZnO emissions. The chromaticity of the nanocomposite, from orange to purple and white, is controlled by adjusting the amounts of C-dots through post-impregnation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...