Effects of alkali and ammonium ions in the detection of poly(ethyleneglycol) by alpha-hemolysin nanopore sensor†
Abstract
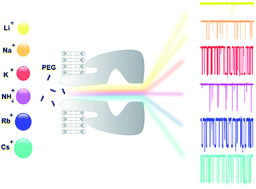
Nanopores have emerged as molecule detectors and more studies are necessary to clarify the analyte–nanopore interaction. Here, we report the influence of cations of the Hofmeister series on a simple bimolecular complexation reaction between poly(ethyleneglycol) (PEG) and α-hemolysin (αHL) nanopore at the single-molecule level. The kinetic constants (on-rate and off-rate) of interaction of PEG molecules with αHL nanopore depend strongly on the type of cation. In the case of on-rate constant, the difference reaches several dozen times. As a consequence of this, both transition rate and detection limit of the nanopore-based sensor were changed. An inverse relationship was demonstrated for the off-rate constant and the solubility of PEG. Except lithium, the other alkali metal cations significantly affect the interaction of PEG with the nanopore and, similarly to potassium, they also bind to this polymer. Thus, the PEG/αHL nanopore interaction can be strongly influenced by the type of cation. The cation-induced specific effect on polymer detection with a single αHL nanopore appears to occur by competition of the cation and PEG by water. Finally, our results represent a guide to select the appropriate physicochemical conditions that enhance the analyte–nanopore interaction, thereby improving the sensitivity of nanopore-based sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...