Gold nanoparticles as potent anticancer agent: green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study†
Abstract
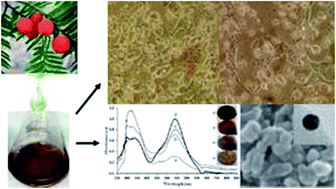
Biogenic high quality colloidal gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), as one of the best anticancer theranostic nanostructures among those reported to date, were synthesized via a simple, efficient and green chemical method using aqueous and ethanolic Taxus baccata extracts and comprehensively characterized by UV-vis spectroscopy, TEM, SEM, AFM, DLS, Zetasizer, EDS, and FT-IR techniques. The AuNPs, encapsulated by the ethanolic compounds of T. baccata with different shapes and uniform size of less than 20 nm and polydispersity index of 0.276, were found completely stable for several months. In consistent with the results of microscopic observations of cell morphology, MTT assay revealed a potent, selective, dose- and time-dependent anticancer activity of AuNPs on the prevalent cancer cell lines including breast (MCF-7), cervical (HeLa) and ovarian (Caov-4), more effective than most of the other reported similar cases. The detailed in vitro investigation of cell exposure by AuNPs, using flow cytometry and real-time PCR, indicated caspase-independent death program as most probable anticancer mechanism of AuNPs. The overall results firmly indicated that the organic compounds of T. baccata, as appropriate reducing and stabilizing agents, not only significantly affect the physicochemical properties of AuNPs but also led to the green synthesis of potent anticancer agent with high potential for cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...