The electrochemical sensor based on electrochemical oxidation of nitrite on metalloporphyrin–graphene modified glassy carbon electrode†
Abstract
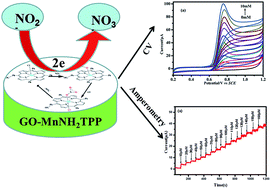
In this study, 5-(4-aminophenyl)-10,15,20-triphenylporphyrin]Mn(III) (MnNH2TPP) and graphene oxide (GO) composite materials (GO–MnNH2TPP) were successfully used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GC) by the drop casting method. The GO–MnNH2TPP/GC composite electrode was used to investigate the electrocatalytic oxidation features of nitrite ion by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and amperometric I–T curve techniques. These experimental results show the GO–MnNH2TPP/GC composite electrode has excellent electrocatalytic performance for the detection of nitrite. The oxidation peak current of nitrite ion at the GO–MnNH2TPP/GC composite electrode has shifted negatively and the intensity of the oxidation peak current increased greatly compared with that at the GC, GO/GC and MnNH2TPP/GC electrodes. A linear relationship has been established between the oxidation current and the nitrite ion concentration. The detection limit of the GO–MnNH2TPP/GC composite electrode for the detection of nitrite ion was found to be 1.1 μM and 2.5 μM (S/N = 3) using CV and amperometric I–T curve techniques, respectively. The GO–MnNH2TPP/GC electrode possesses excellent electrocatalytic activity, rapid response time, low detection limit, high selectivity for nitrite and was applied to the detection of nitrite in real water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...