Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on ferroferric oxide nanoparticles doubly coated with chitosan and β-cyclodextrin in layer-by-layer mode for the separation of ibuprofen
Abstract
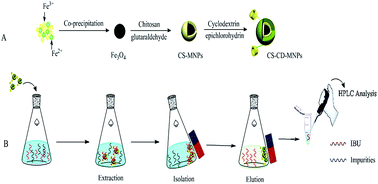
A novel and environmentally-friendly magnetic adsorbent consisting of ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles, β-cyclodextrin and chitosan was successfully fabricated by layer-by-layer methodology and applied in the magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of ibuprofen. The adsorption results demonstrated that ibuprofen extraction was significantly pH dependent and the optimal pH value was 5.0, which was mainly ascribed to the electrostatic interaction and inclusion complexes between the adsorbent and ibuprofen. The adsorption kinetics of ibuprofen was found to follow a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic data for ibuprofen adsorption were fitted well by the Freundlich model and the Freundlich constant indicated it was a favorable process. The thermodynamic parameters suggested that the adsorption process was endothermic and spontaneous in nature. Based on the adsorption research, the main factors affecting the MSPE procedure were optimized, including desorption conditions, amount of adsorbents and eluent volume. Under the optimal conditions, the enrichment factor was 182.56. Moreover, the feasibility of the proposed procedure was demonstrated with the extraction and enrichment of ibuprofen from an environmental water sample, and the results indicated that the complex composition of the investigated object did not significantly affect the selectivity of the extraction process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...