Effect of surfactants and halide ions on the adsorption and oxidation of homocysteine at the gold electrode†
Abstract
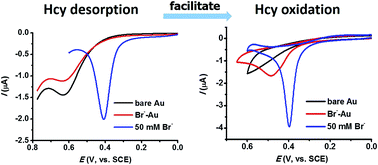
The electro-oxidation of aminothiols such as homocysteine (Hcy) is usually plagued by the large overpotentials required due to the strong irreversible adsorption of the hydrosulfide group on solid electrodes. The present study shows that the sluggish oxidation of Hcy could be greatly facilitated by adsorptive species such as surfactants and halide ions either on the electrode surface or in the electrolyte solution. For example, at a fluorosurfactant-modified Au electrode, Hcy could be oxidized at a very low potential beginning from 0.15 V, and in the presence of 50 mM bromide the oxidation of Hcy features a very sharp and intense oxidation peak at a potential lower than 0.4 V, both of which have never been achieved in earlier reports. To elucidate the mechanism, the effect of these adsorptive species on the adsorption of Hcy at the gold electrode was studied in detail. The results show that these adsorptive species can either reduce the surface coverage of Hcy adsorption at the Au electrode surface, or change the adsorption strength of Hcy with the –COO− group bending toward the electrode surface by –COO− adsorption. The competitive adsorption from surfactants or halide ions moderates the strong adsorption of the hydrosulfide group thus resulting in facile Hcy oxidation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...