Inhibition of fibrillation of human serum albumin through interaction with chitosan-based biocompatible silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
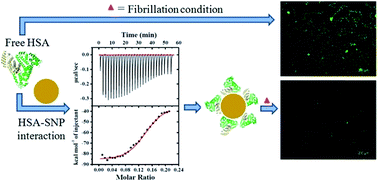
To understand the pharmacokinetics of administered nanomaterials, it is essential to examine the stability and biological activity of proteins by investigating the physicochemical characteristics of the protein–nanoparticle bioconjugate. In this work, the mechanistic detail of the interaction between human serum albumin (HSA) and silver nanoparticles synthesized using nontoxic and biodegradable chitosan as a reducing and stabilizing agent, have been investigated at the nanobio interface. A combination of spectroscopic, calorimetric, and microscopic techniques have been employed to monitor the interaction process. The results illustrate that the chitosan-mediated silver nanoparticles spontaneously bind to HSA without appreciable conformational changes of the protein. Furthermore the potential of the nanoparticles to inhibit the formation of HSA amyloid-like fibrils, in vitro, has been analyzed using thioflavin T fluorescence, circular dichroism, fluorescence microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The experimental observations indicate that interactions between HSA and chitosan-based silver nanoparticles have led to appreciable reduction in amyloid fibril formation. Additionally, cytotoxicity and hemolytic assays are performed to ensure the biocompatibility of the nanoparticles within the application limit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...