Carbon–carbon bond formation in acid deep eutectic solvent: chalcones synthesis via Claisen–Schmidt reaction†
Abstract
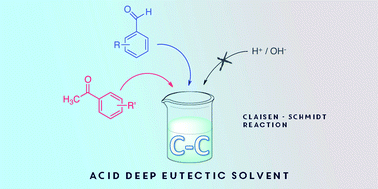
One of the most studied properties of novel organic solvents is represented by their use as media for many chemical reactions. In this field Ionic Liquids (ILs) and more recently Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) have been playing significant roles for their smart properties. DESs are increasing their relevance thanks to their low toxicity, and because of their simple and cheap preparation that can be carried out by simply mixing two compounds. In this work we present the studies of the use of an acid DES obtained from 3-(cyclohexyldimethylammonio)propane-1-sulfonate and (1S)-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid (SB3-Cy/CSA) as reaction media and catalyst for carbon–carbon bond formation reaction via Claisen–Schmidt condensation. This powerful and widely used aldol condensation was performed without the use of any catalysts that are usually needed in this reaction, because of the presence of acid CSA in the DES components. We synthesised fourteen substituted chalcones from benzaldehydes and substituted benzaldehydes in combination with acetophenone and substituted acetophenones as probe reactions. The advantages of the use of this DES in this relevant reaction are represented by: the green properties of the media and its low toxicity; the absence of harmful acids to catalyse the aldol condensation because of the camphorsulfonic acid composing the DES mixture; the recycling and the re-use of the DES in subsequent reaction cycles; the mild conditions and the excellent conversions and yields observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...