Synthesis of a low-density biopolymeric chitosan–agarose cryomatrix and its surface functionalization with bio-transformed melanin for the enhanced recovery of uranium(vi) from aqueous subsurfaces†
Abstract
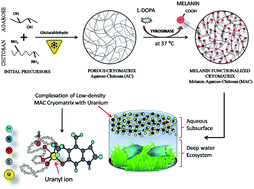
This study presents the development of a biopolymeric cryomatrix for the recovery of uranium from aqueous subsurfaces. The agarose–chitosan (AC) cryomatrix was synthesized by the process of cryotropic-polymerization at −20 °C. The surface of the AC cryomatrix was further modified by green-chemistry using sequential conversion of L-Dopa to melanin through the biocatalytic activity of tyrosinase that was extracted from the corm of plant tuber Amorphophallus campanulatus. Functionalization of the AC cryomatrix with melanin (MAC cryomatrix) presented enhanced uranium uptake, resistance to degradation along with high thermal and mechanical stability. This cryomatrix showed high interconnected porosity (∼90%), high swelling kinetics and permeability. The optimized ratio of biopolymers and cryogenic parameters led to formation of a buoyant low-density matrix that is favorable for radionuclide recovery from subsurface of contaminated water. Maximum uranium adsorption of the melanin-functionalized agarose–chitosan (MAC) cryomatrix was 97% ± 2% observed at pH 5.5 and the qmax was 435 mg g−1. The thermodynamic parameters suggest passive endothermic adsorption behavior. Furthermore, changes in the rheological properties after uranium binding were studied by micro-rheometry. The binding of uranium and chemical attraction in these cryomatrices was confirmed by FTIR. HCl was found to be an efficient eluent for uranium desorption (92 ± 4%) from the MAC cryomatrix. Five repeated cycles of adsorption–desorption showed the reusability of the MAC cryomatrix. These results suggest stability of the low-density MAC cryomatrix under environmental conditions with the potential for recovery of uranium from contaminated aqueous subsurfaces, including seawater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...