Excellent microwave absorption properties of Fe ion-doped SnO2/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites
Abstract
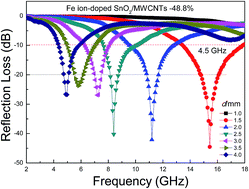
In this work, Fe ion-doped SnO2/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) composites were synthesized using a hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction, TEM, Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and vector network analyses were conducted to demonstrate the structure, interaction, morphology, chemical content, and electromagnetic parameters of the Fe ion-doped SnO2/MWCNTs composites. The as-structured Fe ion-doped SnO2/MWCNTs composites were proven to be outstanding lightweight microwave absorbers when the Fe ion doping percentage was relatively high. Fe ion doping at a molar percentage of 48.8% resulted in a maximum reflection loss (RL) of −44.5 GHz at 15.44 GHz with a layer thickness of 1.5 mm. The maximum RL ≤ −10 dB reached 4.5 GHz at the Ku band. The excellent microwave absorption of the as-prepared composites was principally due to proper attenuation and impedance matching, electric polarization, interfacial polarization, and conductive network. Such composites may have further applications in microwave absorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...