Efficient alternating copolymerization of sulfur dioxide with cyclohexene oxide and a mechanistic understanding
Abstract
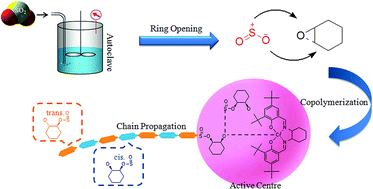
The alternating copolymerization of sulfur dioxide with epoxides is rarely reported because of the low reactivity and polysulfite selectivity of the process. This work describes an efficient alternating copolymerization of sulfur dioxide with cyclohexene oxide using salenCrIIICl as the catalyst. The effect of temperature, time, and type of catalyst on the overall activity and selectivity was investigated in detail. The results proved that the reactivity and polysulfite selectivity of salenCrIIICl are better than those of amines and inorganic salts. The copolymer product poly(cyclohexene sulfite) was characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis and gel permeation chromatography. We found that SO2 not only acts as reactant, but also acts as a co-catalyst to promote the copolymerization reaction in the presence of salenCrIIICl. On the basis of the copolymerization mechanism of CO2 and epoxide using a salen catalyst, and spectroscopic evidence, a mechanism to account for the results is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...