Bis-arylsulfenyl- and bis-arylselanyl-benzo-2,1,3-thiadiazoles: synthesis and photophysical characterization†
Abstract
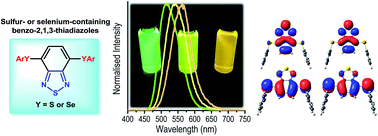
Bis-arylsulfenyl- and bis-arylselanyl-benzo-2,1,3-thiadiazoles were synthesized in good yields by copper-catalysed cross-coupling reaction of arylthiols or diaryl diselenides with the commercially available 4,7-dibromobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole. The arylsulfenyl derivatives present absorptions in the visible region (∼420 nm) with molar absorptivity coefficient and radiative rate constant values ascribed to spin and symmetry allowed π–π* electronic transitions, with almost complete absence of solvatochromic effect. An emission located in the cyan green to green region (514–570 nm), with a large Stokes shift (90–146 nm) was observed, probably associated to the charge transfer character of the S1 state. Theoretical calculations were also performed in order to study the geometry, charge distribution and photophysical properties of the molecules in their ground and excited electronic states. TD-DFT calculations were performed using the PBE1PBE and CAM-B3LYP functionals with cc-pVDZ basis set for geometrical optimisations in the S0 and S1 states and jun-cc-pVTZ basis set to obtain vertical transition energies and electronic properties. Solvent effects were included by IEF-PCM formalism using solvents with different dielectric constants. The computationally predicted transition energies calculated with CAM-B3LYP are in good agreement with the experimental results. No substantial solvatochromic effect was found in the absorption maxima, but in the emission from S1 state a redshift was observed on increasing the solvent polarity. This fact, combined with higher dipole moment in the first excited state and some spatial separation of HOMO and LUMO orbitals could indicate an intramolecular charge transfer character of the S1 state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...