Fullerenol nanoparticles as a new delivery system for doxorubicin†
Abstract
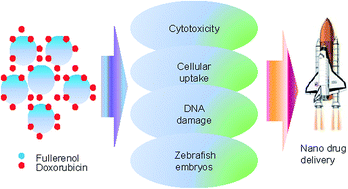
Doxorubicin is a very potent chemotherapeutic drug, however its side effects limit its clinical use. The aim of this research was to investigate the properties of a fullerenol/doxorubicin nanocomposite, its potentially cytotoxic and genotoxic effects on malignant cell lines, as well as its toxicity towards zebra fish embryos. Chromatographic, NMR and mass spectral analysis of the nanocomposite imply that interactions between doxorubicin and fullerenol are non-covalent bonds. The stability of the nanocomposite was confirmed by the use of atomic force microscopy, dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy. The nanocomposite, compared to the free doxorubicin at equivalent concentrations, significantly decreased the viability of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The flow cytometry results indicated that doxorubicin-loaded fullerenol could remarkably increase the uptake of doxorubicin suggesting that fullerenol might be a promising intracellular targeting carrier for the efficient delivery of antitumor drugs into tumor cells. The nanocomposite also affected cell cycle distribution. A genotoxicity test showed that the nanocomposite at all examined concentrations on MCF-7 and at lower concentrations on MDA-MB-231 cells caused DNA damage. Consequently, cell proliferation was notably reduced when compared with controls. Results of the zebrafish embryotoxicity assay showed a decreased overall toxicity, particularly cardiotoxicity and increased safety of the nanocomposite in comparison to doxorubicin alone, as manifested by a higher survival of embryos and less pericardial edema.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...