Effects of optical and magnetic fields on the electrical characteristics of colloidal graphene quantum dots†
Abstract
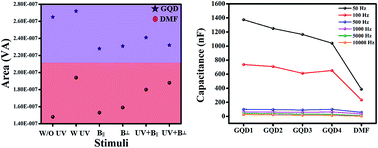
The effects of optical and magnetic fields have a pronounced influence on the electrical performance of graphene quantum dots (GQDs). Nonlinear current–voltage hysteresis during a voltage sweep is revealed due to the charge traps by adsorbates present on the quantum dot (QD) surface. Hence, a polarization dependent variation in QDs even in the presence of the surrounding medium presented an interesting variation in the electrical conductivity. Furthermore, a study of capacitance with frequency revealed that the microwave heating time (MHT) during the preparation of GQDs greatly affected the capacitance value of the colloidal QDs owing to size variation where larger QDs arising from a greater MHT showed lower capacitance and vice versa.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...