An amperometric glucose biosensor based on a MnO2/graphene composite modified electrode
Abstract
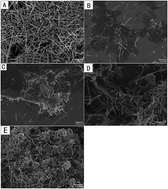
In this paper, a novel composite of graphene/MnO2 (GR/MnO2) was successfully synthesized by a simple one-step hydrothermal method. The as-synthesized MnO2 and the composite were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The results showed that MnO2 was nanorods and the two materials were perfectly composited. The composite was decorated on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) and used for the entrapment of glucose oxidase (GOD). Electrochemical results showed that the composite modified electrode showed a pair of well-defined redox peaks, and the direct electron transfer between GOD and the electrode surface was accelerated. The sensor fabricated by the composite modified electrode showed an excellent response to the oxidation of glucose with a wide linear range (0.04 to 2 mM), low detection limit (10 μM), and high sensitivity (3.3 μA mM−1 cm−2). The sensor also exhibited excellent reproducibility, stability and selectivity, and it can be used in the determination of glucose in real samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...