Ultrafast synthesis of stabilized gold nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extract of Limonia acidissima L. and conjugated epirubicin: targeted drug delivery for treatment of breast cancer†
Abstract
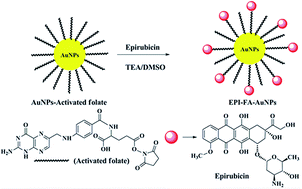
In this study, a green chemistry approach was used for the quick synthesis (within 30 seconds) of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) by using the fruit extract of Limonia acidissima L. The study focused on the formation of L. acidissima L. stabilized AuNPs without using any catalytic agent. The synthesis of the AuNPs was confirmed by observation of the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) band at 537 nm. On the surface of these capped AuNPs, epirubicin (EPI) was conjugated along with activated folic acid (FA) for targeted drug delivery. The EPI–FA–AuNPs complex was characterized using FTIR and a UV-visible spectrophotometer and the AuNPs were characterized by HR-TEM, particle size analyzer, and zeta potential measurements. In vitro stability experiments revealed that the AuNPs were stable in physiological conditions. The in vitro cytotoxicity of free EPI and EPI–FA–AuNPs was investigated against MCF-7 cells, and the results showed that 50% of EPI–FA–AuNPs was enough to achieve inhibition of growth (IC50) and that the amount was lower than that of free EPI. Flow cytometry analysis showed significant reduction in G2/M cells after treatment with EPI–FA–AuNPs, and molecular levels of apoptosis were studied using western blotting. Overall, the results revealed that the EPI–FA–AuNPs have better regression activity on tumor cells than free EPI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...