Core–shell structured nanocomposites Ag@CeO2 as catalysts for hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol and 2-nitroaniline†
Abstract
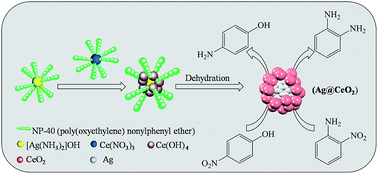
Ag–CeO2 nanocomposites (Ag@CeO2 NCs) with a core–shell structure have been successfully synthesized through the combination of a redox reaction and the reverse micelle technique without any additional reductants or surfactants. Under a N2 atmosphere, the redox reaction automatically occurs between Ag+ and Ce3+ in an alkaline solution, resulting in the formation of Ag@CeO2 NCs by the self-assembly process. By using the XRD, FE-SEM, TEM, XPS, and ICP methods, the characterized results of Ag@CeO2 NCs show that Ag nanoparticles (NPs) with a diameter of 3–7 nm are surrounded by CeO2 NPs. Compared to CeO2 supported Ag NPs, free Ag NPs, and CeO2, the as-synthesized Ag@CeO2 NCs exhibit a superior catalytic activity and high sustainability for the hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol (C6H5NO3, 4-NP) and 2-nitroaniline (C6H6N2O2, 2-NA) with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in water solution at room temperature. The Ag@CeO2 NCs can achieve a complete reduction of 4-NP and 2-NA with turnover frequencies (TOF) of 138.7 and 109.8 h−1, respectively. The durability tests show that the Ag@CeO2 NCs are still highly active for the reduction of 4-NP and 2-NA, preserving 98% and 95% of their initial catalytic activity even after ten runs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...