Biomass-derived multifunctional TiO2/carbonaceous aerogel composite as a highly efficient photocatalyst†
Abstract
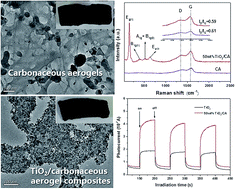
Recently, the development of porous carbon materials driven by environmentally friendly natural biomass has been attracting tremendous focus. Herein, we present a facile and green approach to fabricate a binary TiO2/carbonaceous aerogel (TiO2/CA) composite using wintermelon as the source material via the well-established hydrothermal process. The obtained sponge-like carbonaceous aerogel (CA) has a three-dimensional (3D) porous structure making it a good scaffold for synthesizing the composite. The experimental results show that the TiO2 nanoparticles were homogeneously anchored on the surface of the CA and the composite exhibited outstanding photodegradation capacities for organic pollutants. The enhanced photodegradation capacity could be ascribed to the synergetic properties of the TiO2 photocatalyst and the porous CA support. These findings successfully open up a new fabrication strategy to prepare other 3D structure possessing composites combined with carbonaceous aerogels and show the possibility for the preparation of various composites for multiple applications in various other fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...