Electrocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen in aqueous solution by a cobalt-doped modified lead dioxide electrode: influencing factors and energy demand
Abstract
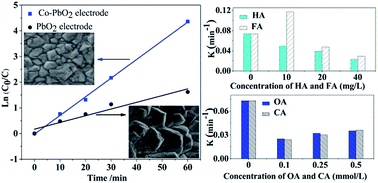
A Co-doped modified PbO2 electrode was prepared to electrocatalytically oxidize IBU in aqueous solution. The effects of initial IBU concentration (40–320 mg L−1), initial pH (4–10), current density (3–30 mA cm−2), natural organic matter and small molecular organic acid were investigated. The structure, morphology and electrochemical properties of the electrode were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, linear sweep voltammetry and cyclic voltammograms. The doping of Co may decrease the particle size and increase the lifetime of PbO2, which favors the electrocatalytic activity. The results indicated that the Co-PbO2 electrode exhibited a highly effective oxidation capacity for IBU. After 60 min of electrolysis, the removal of IBU and COD at a current density of 3 mA cm−2 for 80 mg L−1 of IBU reached 98.7% and 32.1%, respectively, and the degradation of COD was 53.6% after 180 min of reaction. The reaction apparently followed a first-order kinetics model. When the IBU initial concentration was 80 mg L−1, the highest reaction rate and energy efficiency were observed. Considering the energy demand and space efficiency, the applied current density of 3 mA cm−2 was the most suitable. Lower pH favored degradation because the oxygen evolution reaction was restrained. The addition of low concentrations (10 mg L−1) of humic acid and fulvic acid could promote the degradation of IBU, whereas high concentrations (20–40 mg L−1) inhibited the degradation of IBU. Moreover, the addition of oxalic acid and citric acid (0.1–0.5 mmol L−1) could inhibit IBU degradation. Finally, the possible reaction pathways were proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...