Non-covalent dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution with hyperbranched polyethylene-g-poly(methacrylic acid)†
Abstract
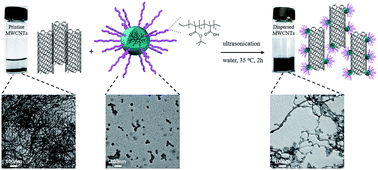
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have great potential applications in biomedical materials. However, the poor solubility of CNTs in water hinders their practical applications. Thus, an amphiphilic hyperbranched polyethylene-g-poly(methacrylic acid) (HBPE-g-PMAA) was synthesized to improve the solubility of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) in water. The HBPE segment provided the CH–π interactions between HBPE and MWCNTs, while the PMAA segment gave the de-bundled MWCNTs good solubility and stability. In this way, the bundled MWCNTs were found to be dispersed efficiently into individual nanotubes by the HBPE-g-PMAA. The dispersing efficiency of MWCNTs was evaluated by TGA, TEM, SEM and AFM. The maximum concentration of MWCNTs was found to be 135 mg L−1. Hence, the HBPE-g-PMAA was an efficient amphiphilic polymer-based dispersant for dispersion of MWCNTs in water, and might find potential application in biomedical systems and devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...