Cancer theranosis using mono-disperse, mesoporous gold nanoparticles obtained via a robust, high-yield synthetic methodology†
Abstract
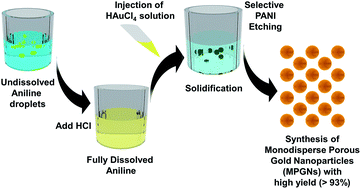
Porous noble metal nanoparticles exhibit many attractive nanoplasmonic features, and these structures have potential applications in many fields. However, such applications have been hindered by a lack of synthetic methods with the ability to mass-produce mono-disperse nanoparticles. Current synthetic approaches to porous gold nanostructure fabrication involve galvanic replacement approaches or electrochemical deposition methods that are generally limited by stringent multi-step protocols and relatively low yields. Here, we introduce the facile synthesis of scalable, mono-disperse, mesoporous gold nanoparticles (MPGNs) using an acidic emulsification method. This method facilitates high synthetic yields (>93%) and tunable particle sizes (130–400 nm). MPGNs exhibit enhanced payloads of gadolinium (Gd), a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Additionally, they permit photo-thermal conversion under near-infrared light (NIR) irradiation due to the increased surface area to volume ratio and the unique, structure-mediated LSPR effect. Specifically, MPGNs fabricated using our method provided Gd payloads 2–4 orders of magnitude greater than previously reported theranostic nano-probes. We believe that our novel synthetic technique will not only contribute to large-scale production of homogeneous porous gold nanoparticles, but will also promote further research in porous noble metal nanostructures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...