Antidiabetic activity of silver nanoparticles from green synthesis using Lonicera japonica leaf extract
Abstract
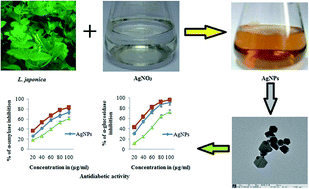
In this work we report the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using the aqueous leaf extract of Lonicera japonica. A color change from pale yellow to brown was observed during the synthesis process. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) studies show an absorption band at 435 nm due to surface plasmon resonance of the AgNPs, further characterized using the average size and stability of the AgNPs, which were 53 nm and −35.6 mV as determined by a zeta sizer. The spherical, hexagonal shape and the face centered cubic crystalline structure of metallic silver were confirmed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The functional group of biomolecules present in the AgNPs was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR). The synthesized AgNPs exhibited strong antioxidant activity. The antidiabetic ability of AgNPs was shown by the effective inhibition against carbohydrate digestive enzymes such as α-amylase and α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 54.56 and 37.86 μg mL−1, respectively. The inhibition of the kinetic mechanism was analyzed with LB and Dixon plots. AgNPs were identified to be reversible noncompetitive inhibitors and Ki values of 25.9 and 24.6 μg were found for key enzymes of diabetes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase). We conclude that the results suggest that the AgNPs were found to show remarkable potential antidiabetic activity against the key enzymes of diabetes and were found to be an appropriate nanomedicine for nanobiomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...