Ca-doped CuS/graphene sheet nanocomposite as a highly catalytic counter electrode for improving quantum dot-sensitized solar cell performance
Abstract
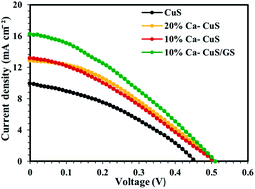
Copper sulfide (CuS) is one of the most important counter electrodes (CEs) in high-efficiency, quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs). In this work, we investigated the effect of Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba ion incorporation into the CuS layer on the photovoltaic performance of quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Metal ion-doped CuS was deposited by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method on the FTO substrate. As a result, the quantum dot photoanode with the optimized Ca-doped CuS CE exhibited power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 2.33%, which is much higher than bare CuS CE (PCE 1.68%), Ba-doped CuS (1.81%), Mg-doped CuS (1.82%) and Sr-doped CuS (1.67%). A sandwiched structural Ca-doped CuS/graphen sheet (Ca-doped CuS/GS) electrode was prepared by repeating electrophoretic deposition (EPD) of graphene sheets and deposition of Ca-doped CuS nanoparticles. When a Ca-doped CuS/graphene sheet (Ca-doped CuS/GS) was used as a CE, the QDSSC exhibited higher power conversion efficiency (2.73%) compared to cells with Ca-doped CuS (2.33%) and bare-CuS (1.68%) cathodes. A full description of reasons for efficiency enhancement are discussed in this paper by using diverse electrochemical and spectral analyses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...