Platycodin D inhibits B16F10 melanoma metastasis via antiangiogenic activity
Abstract
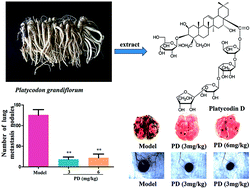
Platycodin D (PD) is an active component that is mainly isolated from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum, and it has been suggested to exhibit anticancer activities. In this study, anti-B16F10 melanoma metastasis activities of PD and related antimetastasis mechanisms were investigated in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, PD altered the cytoskeleton of B16F10 cells and inhibited B16F10 cell viability, as well as cell adhesion on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), cell migration, and cell invasion. Moreover, PD inhibited the ability of HUVECs proliferation and tube formation. Further more, PD exhibits non-toxic and good biocompatibility under certain concentrations (20 μg mL−1). In vivo, PD (3 and 6 mg kg−1) inhibited B16F10 cell lung metastasis and tumour angiogenesis in an experimental lung metastasis mouse model. In addition, PD significantly decreased the levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and increased the serum levels of cytokines including interleukin-12 (IL-12), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in experimental mice. Taken together, these results clearly indicated that PD inhibited B16F10 melanoma metastasis via antiangiogenic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...